Amazon Virtual Private Cloud Connectivity Options Whitepaper (2018)
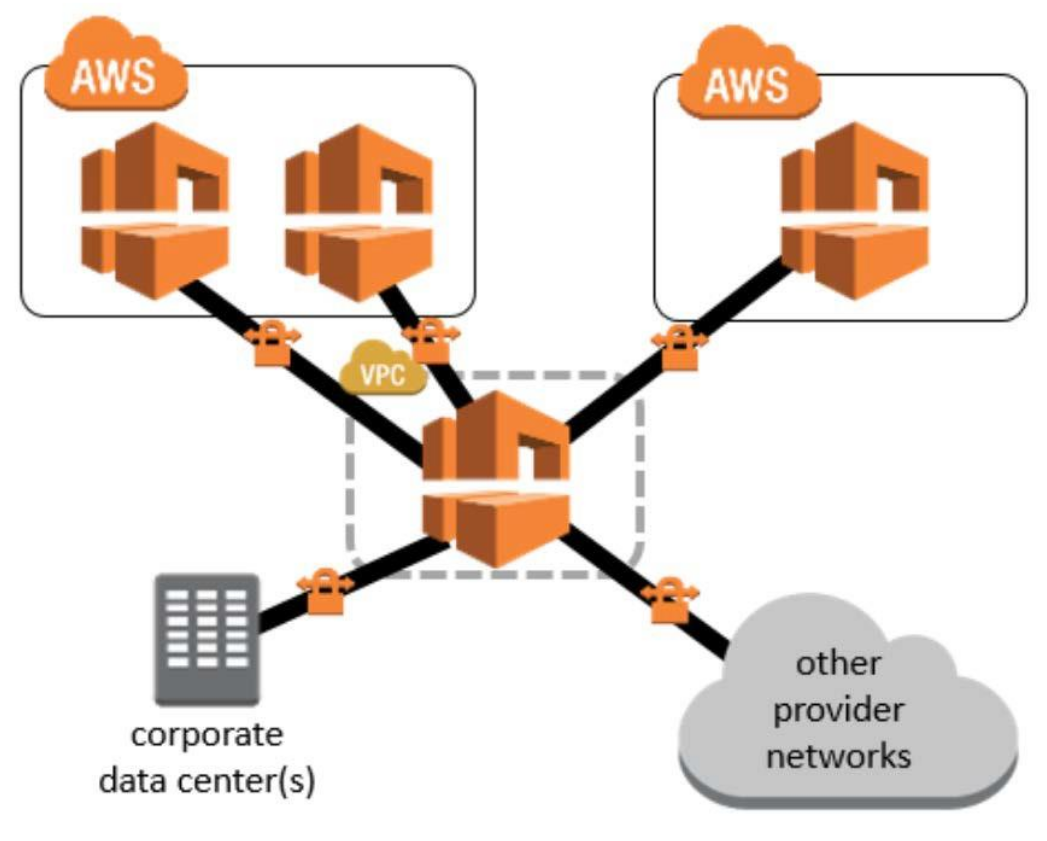
Network-to-Amazon VPC Connectivity Options
AWS Managed VPN
- AWS managed IPSec VPN connection over the internet
- Advantages
- Reuse existing VPN equipment and processes
- Reuse existing internet connections
- AWS managed endpoint include multi-data center redundancy and automated failover
- Supports static routes and BGP peering and routing policies
- Limitations
- Network latency, variability and availability
- Customer managed endpoint for implementing redundancy and failover
- Customer device must support BGP if required
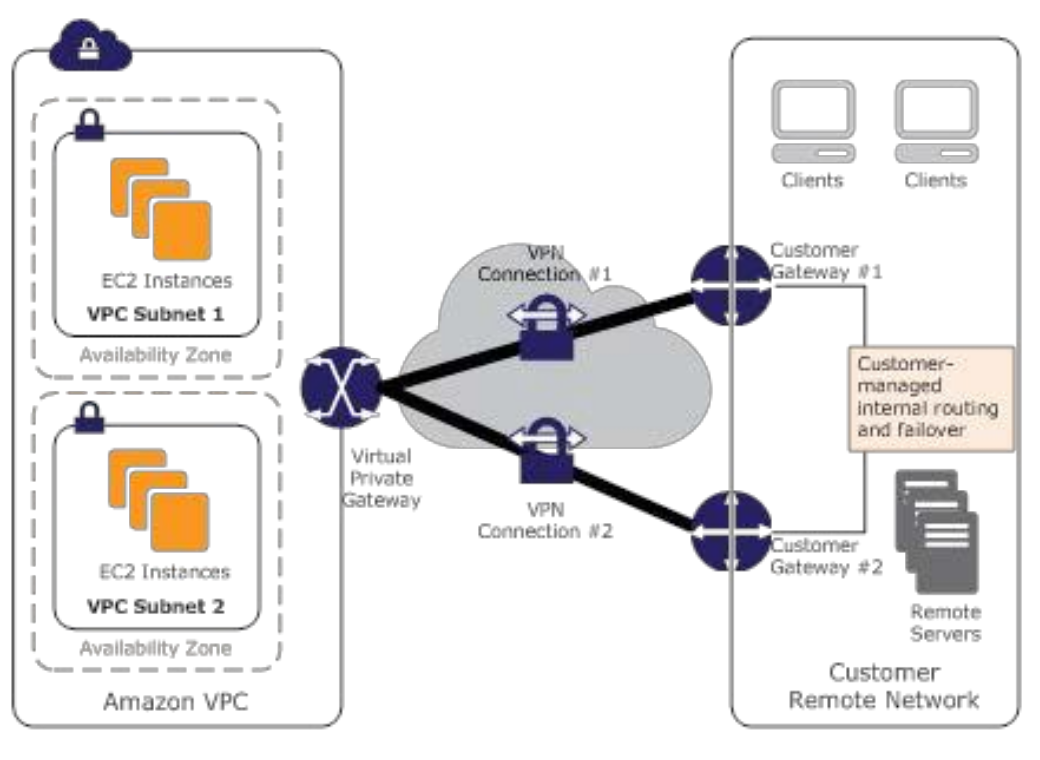
Redundant AWS managed VPN connections
AWS Direct Connect
- Dedicated network connection over private lines
- Advantages
- More predictable network performance, reduced bandwidth cost
- 1 or 10 Gbps provision connections
- Supports BGP peering and routing policies
- You can connect to VPCs in different regions using AWS Direct Connect Gateway
- Disadvantages
- May require additional telecom and hosting provide relationship or new network circuits to be provisioned
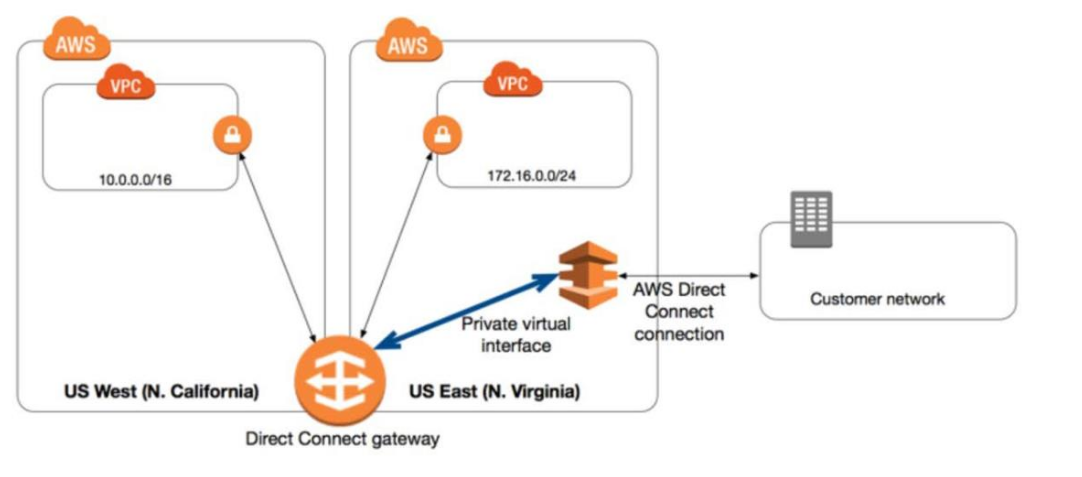
AWS Direct Connect Gateway
AWS Direct Connect + VPN
- IPSec VPN connection over private lines
- Advantages
- AWS Direct Connect features with the addition of secure IPSec VPN connection
- Disadvantages
- Additional VPN complexity added on top of AWS Direct Connect
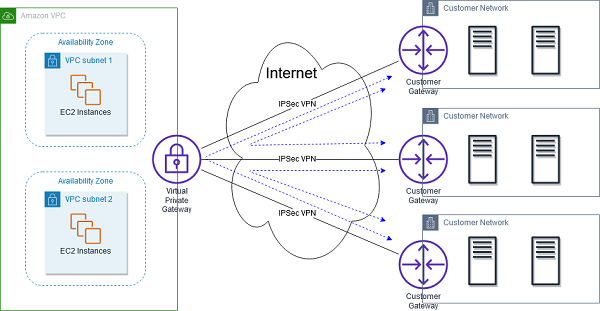
AWS VPN CloudHub
- Connect remote branch offices in hub-and-spoke model for primary or backup connectivity
- AWS VPN CloudHub leverages an Amazon VPC virtual private gateway with multiple gateways, each using unique BGP autonomous system numbers (ASNs)
- Advantages
- Reuse existing internet connections and AWS VPN connections
- AWS managed virtual private gateway include multi-data center redundancy and automated failover
- Support BGP for exchanging routes and routing policies
- Disadvantages
- Network latency,variability and availability are dependent on the internet
- User managed branch office endpoints are responsible for implementing redundancy and failover
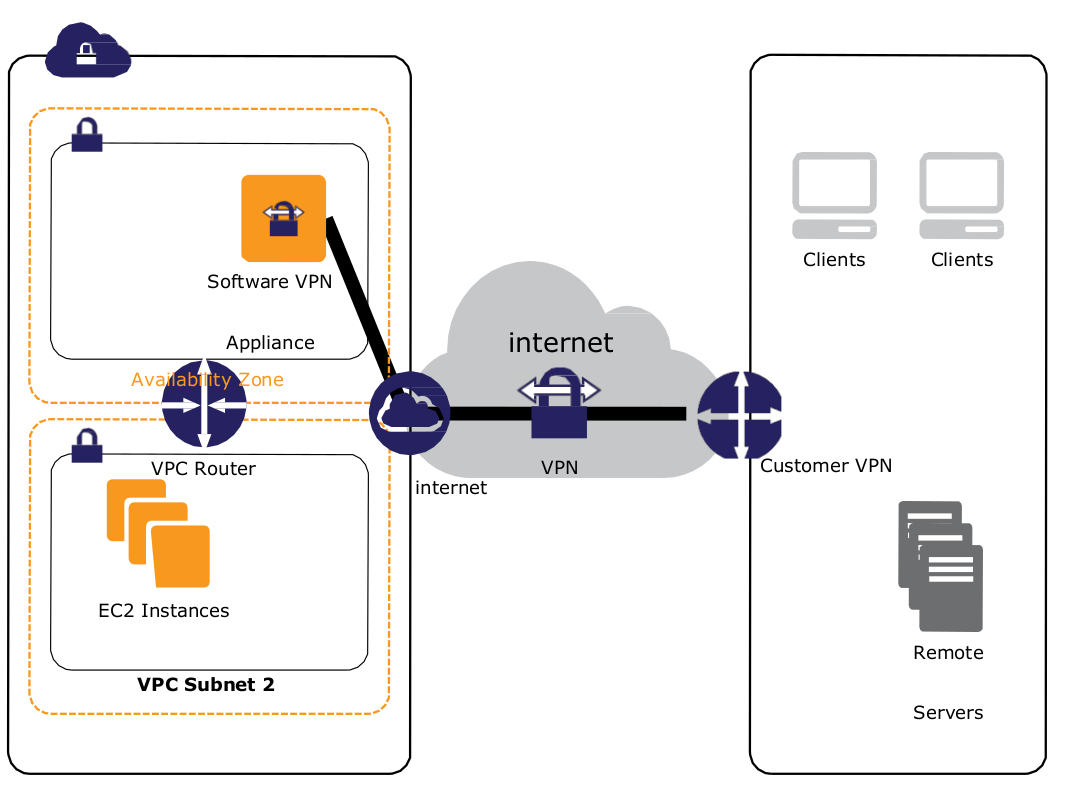
Software VPN
- Software application-based VPN connection over the internet
- Advantages
- Supports a wider array of VPN vendors, products, and protocols
- Fully customer-managed solution
- Disadvantages
- Customer is responsible for implementing HA solutions for all VPN endpoints
Software VPN
Transit VPC
- Software appliance-based VPN connection with hub VPC
- Common strategy for connecting multiple, geographically disperse VPCs and remote networks in order to create a global network transit center
- AWS managed IPSec VPN connection for spoke VPC connection
- Advantages
- Supports a wider array of VPN vendors, products, and protocols
- Fully customer-managed solution
- AWS managed VPN connection between hub and spoke VPCs
- Disadvantages
- Customer is responsible for implementing HA solutions for all VPN endpoints
Software VPN and Transit VPC
Amazon VPC-to-Amazon VPC Connectivity Options
VPC Peering
- AWS-provided network connectivity between two VPCs
- Advantages
- Leverages AWS network infrastructure
- No single point of failure
- No bandwidth bottleneck
- Disadvantages
- VPC peering does nto support transitive peering relationships
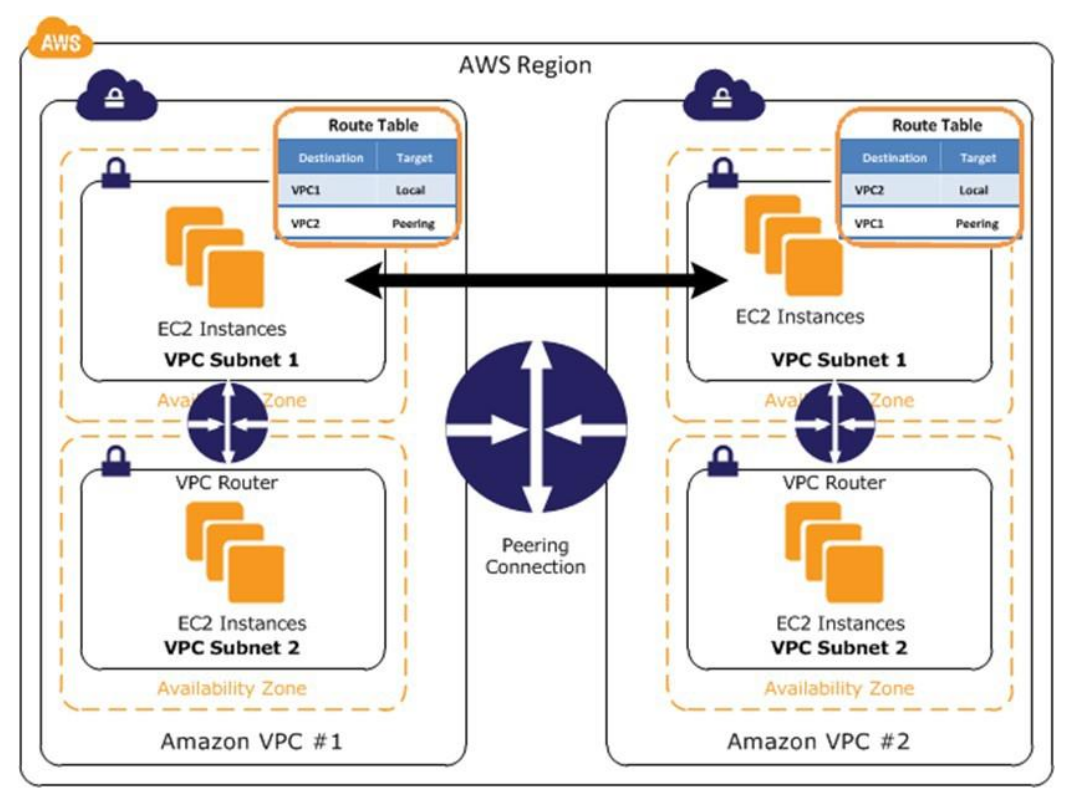
VPC Peering
Software VPN
- Software appliance-based VPN connections between VPCs
- Advantages
- Leverages AWS networking equipment in-region adn internet pipes between regions
- Supports a wider array of VPN vendors, products and protocols
- Managed entirely by you
- Disadvantages
- You are responsible for implementing HA solutions for all VPN endpoints (if required)
- VPN instances could become a network bottleneck
Software-to-AWS Managed VPN
- Software appliance to VPN connection between VPCs
- Advantages
- Leverages AWS networking in-region and internet pipes between regions
- AWS managed endpoint includes multi-data center redundancy and automated failover
- Disadvantages
- You are responsible for implementing HA solutions for the software appliance VPN endpoints (if required)
- VPN instances could become a network bottleneck
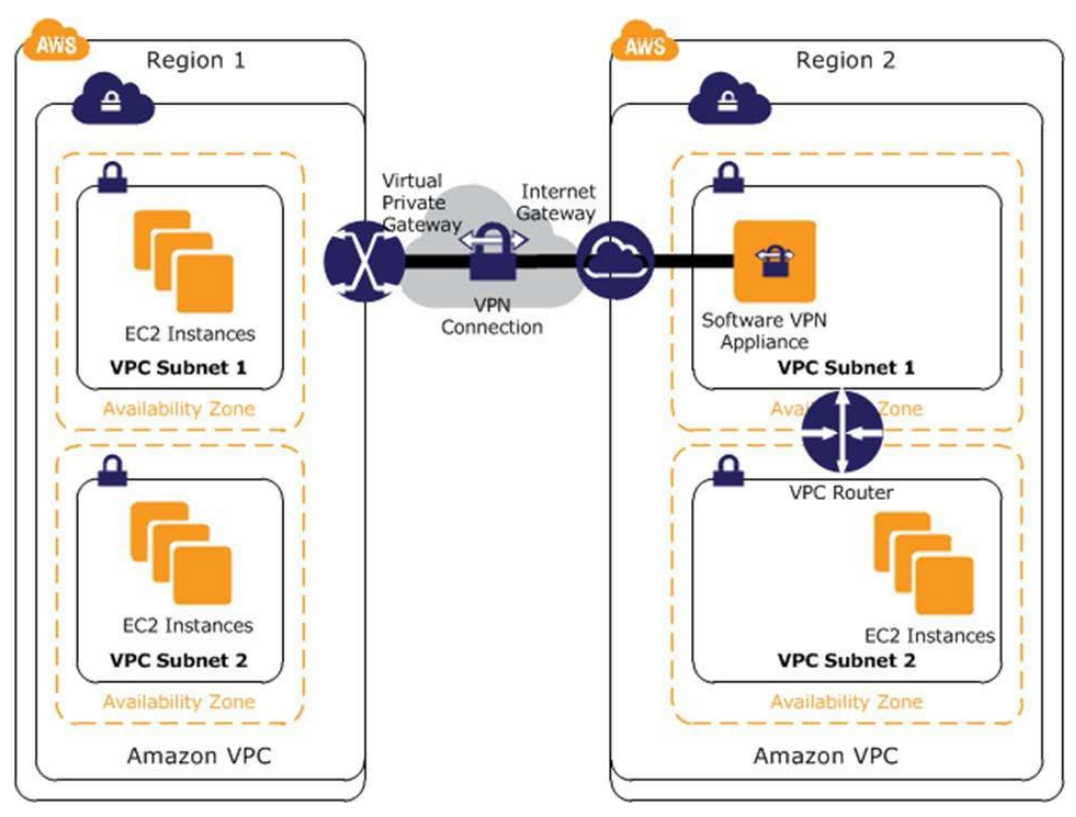
Software to AWS Managed VPN
AWS Managed VPN
- VPC-to-VPC routing managed by you over IPSec VPN connections using your equipment and the internet
- Advantages
- Reuse existing Amazon VPC VPN connections
- AWS managed endpoint include multi-data center redundancy and automatic failover
- Supports static routes and dynamic BGP peering and routing policies
- Disadvantages
- Network latency, variability and availability depends on internet conditions
- The endpoint you manage is responsible for implementing redundancy and failover (if required)
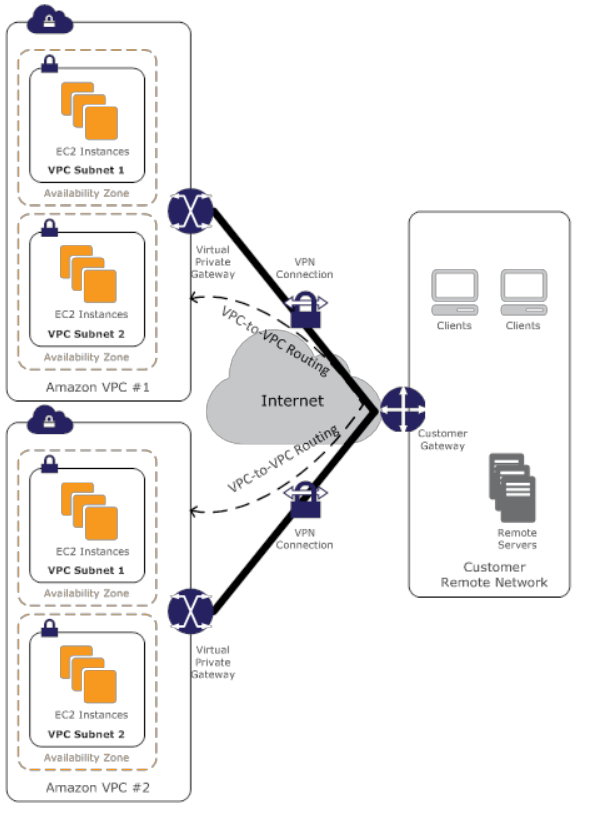
VPC to VPC through AWS Managed VPN
AWS Direct Connect
- VPC-to-VPC routing managed by you using your equipment in an AWS Direct Connect location and private lines
- Advantages
- Consistent network performance
- Reduced bandwidth costs
- Supports static routes and BGP peering and routing policies
- Disadvantages
- May require additional telecom and hosting provide relationships
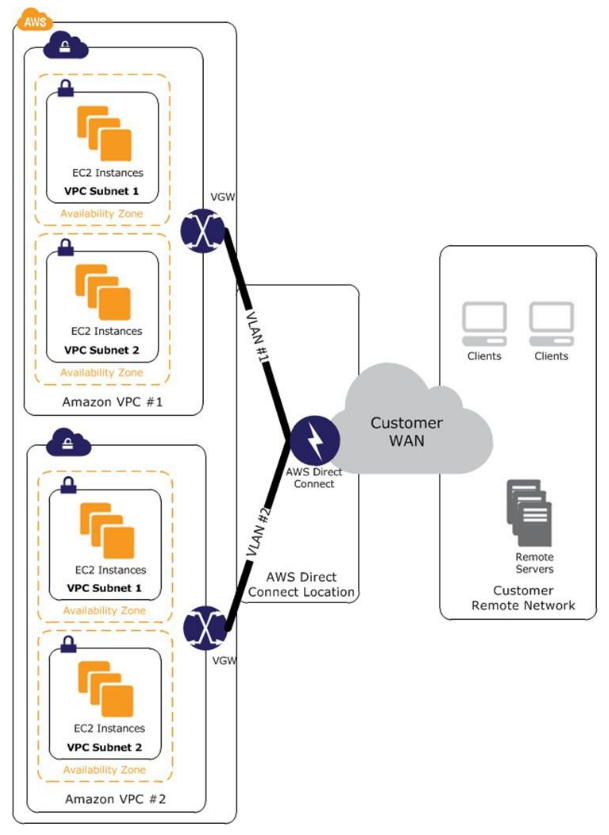
VPC to VPC through AWS Direct Connect
AWS Private Link (VPC endpoint)
- AWS-provided network connectivity between two VPCs using interface endpoints
- Advantages
- Leverages AWS networking infrastructure
- No single point of failure
- Disadvantages
- VPC endpoint services only available in AWS region in which they are created
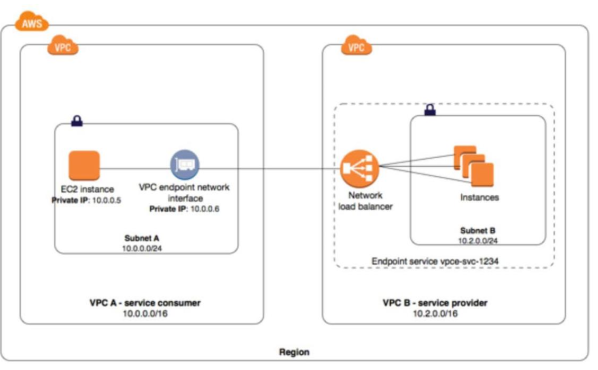
AWS Private Link
Internal User-to-Amazon VPC Connectivity Options
- Virtual extension of your data center into AWS
- Leverages existing end-user internal and remove access policies and technologies
- Requires existing end-user internal and remove access implementations
Software Remote-Access VPN
- Cloud-based remote access solution to Amazon VPC and/or internal networks
- Advantages
- Leverages low-cost, elastic, and secure web services provided by AWS for implementing a remote access solution
- Disadvantages
- Could be redundancy if internal and remote access implementations already exist
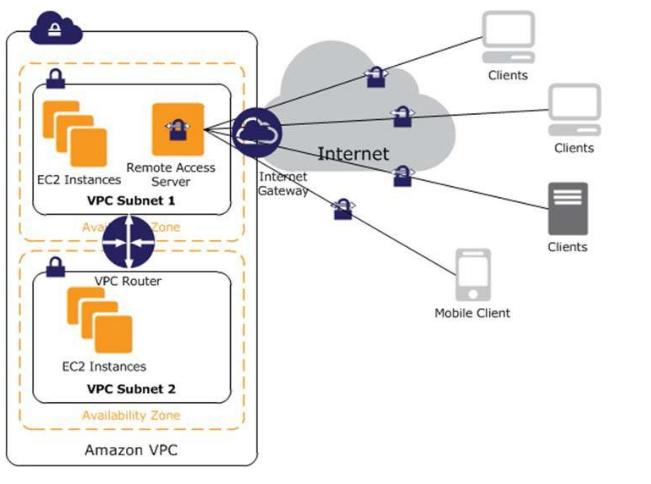
Remote Access VPN Solutions










